In the realm of renewable energy generation, assessing the availability of a utility grid is crucial for accurate energy yield predictions. This article delves into the evaluation of grid availability loss, particularly focusing on Spain, Portugal and France. By mapping various statistics and data sources, we aim to provide a clearer understanding of how grid availability impacts energy production estimations for wind farms.
Understanding grid availability loss
Grid availability loss refers to the reduction in potential energy production due to unavailability of the utility grid. Wind industry assumption: utility companies typically schedule an average of one maintenance outage per year for substations and transmission lines. Depending on various factors, including regional characteristics and levels of transmission system connectivity, this loss can range from 0.1% to 1%, or even higher in certain instances. I t’s important to note that this evaluation does not include technical restrictions related to grid curtailment, which often further complicates the assessment of energy loss.
The importance of accurate loss assessment
In preconstruction studies of energy yield predictions, it is critical to accurately account for grid availability loss. This loss affects the overall efficiency of renewable energy projects, impacting financial forecasts, investment decisions and ultimately the transition to sustainable energy sources. Understanding where and how these losses occur can guide better planning and operational strategies for wind energy operators.
Methodology: Data collection and analysis
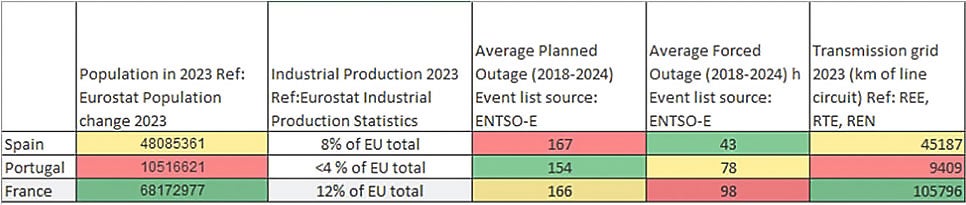
This study concentrates on three countries: Spain, Portugal and France. The evaluation incorporates various country-specific statistics that include:
- Population statistics – Data obtained from Eurostat to provide a demographic overview.
- Industrial production levels – Insights into production capabilities that influence energy demand.
- Transmission grid (km of line of circuit) – Sourced from national transmission system operators such as Red Eléctrica de España (REE), Réseau de Transport d’Electricité (RTE) and Redes Energéticas Nacionais (REN).
- Outage data – Planned and forced outages information were extracted from the European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E).

The collection of these diverse datasets, covering publications from 2018 to 2024, highlights major challenges. One pivotal challenge lies in connecting national-level statistics on grid outages to specific wind farm sites. For example, while Spain experienced extensive planned outages in 2019, it is essential to understand that remote wind farms may not be impacted by outages in other regions.
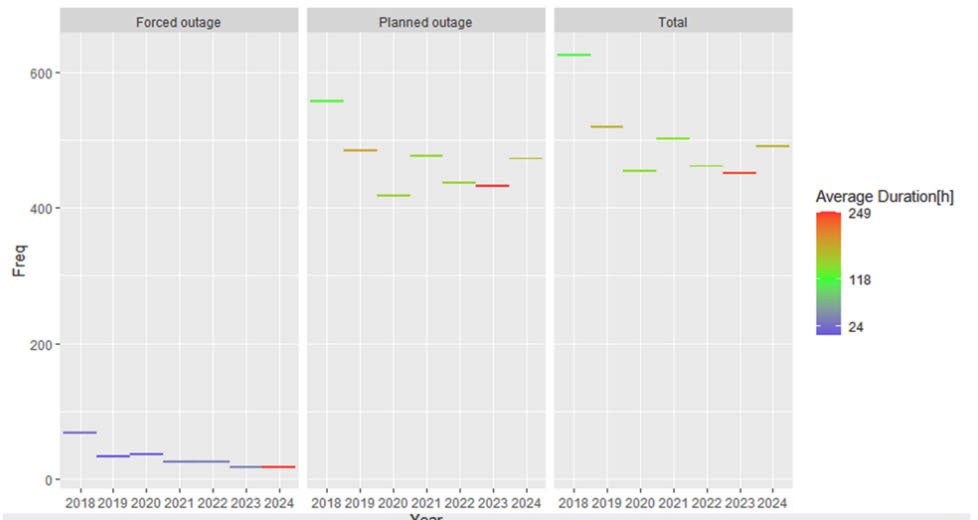
Analysis of outage data
The average outage duration across Spain between 2018 and 2024 was approximately 159 hours, while France reported an average of 160 hours and Portugal 152 hours. This data suggests that, when considering time-based availability, the potential grid availability loss can be around 1.7%. However, these figures represent national statistics. Evaluating them at a regional and wind-farm-specific level can yield more accurate, localized estimates.
Results: Insights on grid availability loss
The findings reveal critical insights into annual and monthly grid availability loss statistics across the three studied countries:
- Spain – The lengthy planned outages in 2019, although significant, did not uniformly affect all wind farms, emphasizing the need for localized analysis.
- France and Portugal – Similar regional disparities exist, highlighting differences based on local grid conditions. The relevance of these losses varies significantly across different wind farm locations.
Strategies for improved assessment
To enhance the reliability of energy yield predictions, a roadmap for defining new strategies for accounting grid availability losses in energy estimation studies is discussed. Some effective strategies may include:
- Implementing monthly profiles – Applying monthly profiling for outages can lead to more dynamic and representative loss calculations, capturing both planned and forced outages more effectively.
- Using public data sources – Harnessing data from public resources can significantly refine energy loss assumptions, thus improving the accuracy of preconstruction energy yield assessments.
Conclusion: Moving forward with grid availability insights
As the renewable energy sector continues to advance, understanding the nuances of grid availability loss becomes paramount. By employing a comprehensive approach to data collection and analysis, stakeholders can obtain a clearer picture of potential energy losses. This understanding not only aids in refining estimation models but also optimizes operational strategies for wind energy projects across Spain, Portugal and France.
In conclusion, accurately mapping grid availability loss is an essential step in the efficiency and success of renewable energy projects. As we move toward a sustainable future, incorporating these insights into our strategies will be vital for maximizing energy production and minimizing losses in the ever-evolving landscape of renewable energy.
Get connected with our sales team
Thanks for your interest in our products and services. Let's collect some information so we can connect you with the right person.





