A management system is about structures, processes, measures and competencies. The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) has published UN Regulation No. 155 (UN R155) requiring automotive manufacturers to implement a cybersecurity management system (CSMS) for all vehicles manufactured in July 2024 or later.
UN R155 CSMS requirements
UN R155 defines a CSMS as “a systematic risk-based approach defining organizational processes, responsibilities and governance to treat risk associated with cyber threats to vehicles and protect them from cyberattacks.”
In other words, the CSMS structures your company's approach to safety and security and governs what actions must be taken by whom and when to keep the connected vehicle secure until the end of its service life. It includes your company’s:
- Cybersecurity culture.
- Organizational structure.
- Documentation of required development processes and procedures.
- Monitoring of whether the work performed is in accordance with established processes and procedures.
- Monitoring of whether the work results in appropriately secure products.
- Necessary infrastructure.
- Required skills and competencies.
The UNECE requires OEMs and suppliers to:
- Design products to be secure throughout their life cycle.
- Constantly evaluate new vulnerability information.
- Take action accordingly.
ISO/SAE 21434: A comprehensive approach to cybersecurity
The international standard ISO/SAE 21434, Road Vehicles — Cybersecurity Engineering, published in 2021, takes a comprehensive approach to connected vehicle cybersecurity and identifies the engineering requirements for a CSMS.
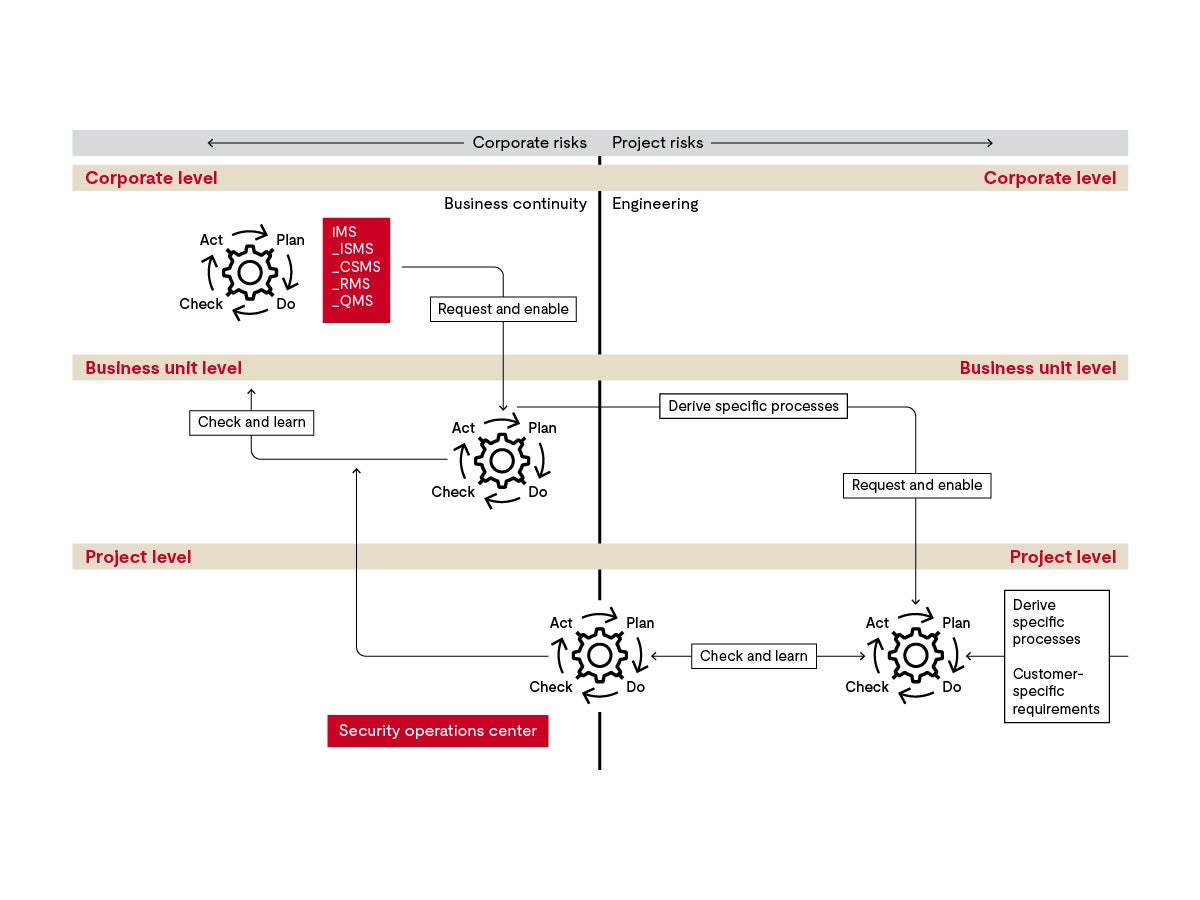
The CSMS coordinates ongoing comprehensive cybersecurity tasks at the corporate, business and project level. Risks differ at each level, and the management system’s level of detail relates to the nature of the risks. At the appropriate levels, companies should derive corresponding subsystems with structures, processes, measures and competencies. Industry best practices recommend integrating cybersecurity requirements into your existing process landscape rather than deploying an additional isolated management system.
Continuous cybersecurity activities
A cybersecurity management system can help companies thoroughly carry out necessary cybersecurity activities for development, production and post-production until the vehicle series reaches the end of its service.
To this end, Clause 8 of ISO/SAE 21434, in particular, requires that manufacturers continually check whether the risk assumptions and countermeasures are up to date.
Carefully implementing the CSMS and fostering a cybersecurity culture in your organization can help your team members more effectively integrate cybersecurity concerns into their work and develop cybersecurity by design.

Cybersecurity services from UL Solutions Software Intensive Systems
UL Solutions Software Intensive Systems can support automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and suppliers in your efforts to:
- Foster awareness for the need for comprehensive end-to-end safeguards.
- Provide detailed assessments of any threats posed.
- Match your cybersecurity policies to processes, products and IT requirements.
- Manage involved specialists.
- Assess and improve your development processes with respect to security issues.
- Adapt existing workflows and procedures to address key cybersecurity issues.
- Navigate conformance to UNECE systems homologation guidelines.
- Define and introduce new development processes that meet the requirements of ISO/SAE 21434.
- Evaluate, develop and implement cybersecurity management systems.
- Select relevant security technology and industry standards according to your requirements (we offer ISO-compliant kits and templates).
Get connected with our team
Thanks for your interest in our products and services. Let's collect some information so we can connect you with the right person.
