
UL Materials Testing and Certification (English)
We offer several types of test methods to test the electric properties of your plastic material.

This method is used to determine the volume resistivity of an insulating material. The surface flows of the test specimen are eliminated using an electrode.
| Test specimen | Ø 80 mm, 2 mm thick |
| Test voltage | Between 1 V and 1,000 V |
| Current measurement | 10-1 A to 10-14 A |
| Temperature range | 23°C to 200°C |
Standards for volume resistivity
UL 746A, ASTM D257, IEC 62631, or equivalent standards
Volume resistivity ρ (rho). This is the volume resistivity of an insulating material in the form of a cube whose edges measure 1 cm.
This method is used to determine the surface resistivity of a test specimen. The volume flows of the insulating material are eliminated using an electrode.
| Test specimen | usually Ø 80 mm, 2 mm thick |
| Test voltage | Between 1 V and 1,000 V |
| Current measurement | 10-1 A to 10-14 A |
| Temperature range | 23°C to 200°C |
Standards for surface resistivity
UL 746A, ASTM D257, IEC 62631, or equivalent standards
This method is used to assess the dielectric strength of an insulating material. It calculates the voltage at which a harmonic alternating voltage collapses upon destruction of the insulating material.
| Test specimen | usually Ø 80 mm, 2 mm thick |
| Max. test voltage | 100 kV (50 Hz) |
| Current on breaking | 40 mA |
| Surrounding medium | Insulating oil |
| Electrode pairs | Plate/plate Ball/ball Ball/plate |
Standards for dielectric strength
IEC 60243-1, VDE 0303-21, UL 746A, or equivalent standards
This method is used to assess the relative resistance of insulating materials to tracking.
This method is used to assess the relative resistance of insulating materials to tracking.
This method can be used to assess the susceptibility to tracking of insulating materials that are exposed to high voltages outdoors.
Insulators installed in the open are often at the mercy of humidity. Their electrical insulation properties can deteriorate to such an extent as a result that tracking paths are formed on the insulator surface. This test determines the tracking resistance that defines the dielectric strength of the insulating material surface and the maximum allowable leakage current (tracking).
| Test specimen | 130 mm x 50 mm x 6 mm |
| Test voltage | 2,5 kV, 3,5 kV, 4,5 kV (50Hz) |
| Test solution | 0,15 ml/min at 2,5 kV 0,30 ml/min at 3,5 kV 0,60 ml/min at 4,5 kV |
| Failure criteria Method A: |
|
| Failure criteria Method B: |
|
The maximum test voltage at which five specimens each resist the stress for six hours without any of the failure criteria being met.
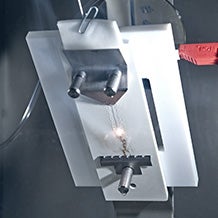

The high-current arc ignition (HAI) test determines the number of arcs which are necessary to ignite a plastic material. This test is carried out on the plastic surface: 40 arcs per minute are ignited between a fixed and a movable electrode.
Standards High-Current Arc Ignition (HAI)
UL 746A

UL Materials Testing and Certification (English)
Thanks for your interest in our products and services. Let's collect some information so we can connect you with the right person.